SpringSchedule配置简单,并且由于属于Spring框架,可以通过Spring来管理bean的生命周期,从而可以降低编程的复杂度,但是SpringSchedule有个问题,就是不支持分布式系统,也就是假如一个项目部署在多台服务器上,那么定时任务会在多台服务器上同时执行,需要自行做分布式控制。
SpringSchedule的使用
以注解配置为例
- 配置文件中添加配置 添加相关注解配置:
xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-3.0.xsd
开启定时任务的注解扫描:
<task:annotation-driven/>
- 为方法添加@Scheduled注解
设置定时任务的方式有两种,一种是配置一定的延时时间以固定频率运行,一种是设置scon表达式
代码分析
主要类:ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 方法调用链:postProcessAfterInitialization()->processScheduled()->TaskSchedule.schedule()
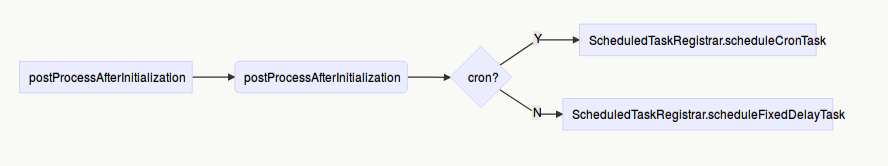
ScheduledTaskRegistrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask实现比较简单,内部通过TaskScheduler的scheduleAtFixedRate方法实现任务的调度,并返回任务结果
而ScheduledTaskRegistrar.scheduleCronTask相对来说较复杂,主要看下TaskScheduler的ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Trigger trigger);方法
根据以上包的结构图来看,TaskScheduler有六个子类,
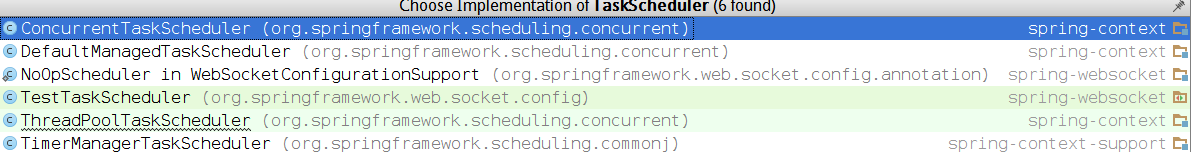
看下ThreadPoolTaskScheduler的schedule方法
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Trigger trigger) {
ScheduledExecutorService executor = getScheduledExecutor();
try {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = this.errorHandler;
if (errorHandler == null) {
errorHandler = TaskUtils.getDefaultErrorHandler(true);
}
return new ReschedulingRunnable(task, trigger, executor, errorHandler).schedule();
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
throw new TaskRejectedException("Executor [" + executor + "] did not accept task: " + task, ex);
}
}
其中的ReschedulingRunnable是一个Runnable的子类,同时也是ScheduledFuture的子类,它的schedule方法如下
@Nullable
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule() {
synchronized (this.triggerContextMonitor) {
this.scheduledExecutionTime = this.trigger.nextExecutionTime(this.triggerContext);
if (this.scheduledExecutionTime == null) {
return null;
}
long initialDelay = this.scheduledExecutionTime.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis();
this.currentFuture = this.executor.schedule(this, initialDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this;
}
}
问题来了,这块代码只看到了执行一次任务,那么后续的任务是怎么触发的?
看this.executor.schedule(this, initialDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS),这里的ReschedulingRunnable同时也是一个Runnable类,当执行调度时,其runnable()方法被执行,再看其runnable()方法
@Override
public void run() {
Date actualExecutionTime = new Date();
super.run();
Date completionTime = new Date();
synchronized (this.triggerContextMonitor) {
Assert.state(this.scheduledExecutionTime != null, "No scheduled execution");
this.triggerContext.update(this.scheduledExecutionTime, actualExecutionTime, completionTime);
if (!obtainCurrentFuture().isCancelled()) {
schedule();
}
}
}
在runnable()方法中,其schedule()方法再次被执行,巧妙。如果不用这种方式实现,还可以怎么实现呢?